Two Physicists Share Nobel Prize For Detecting Changes In Neutrino Identities
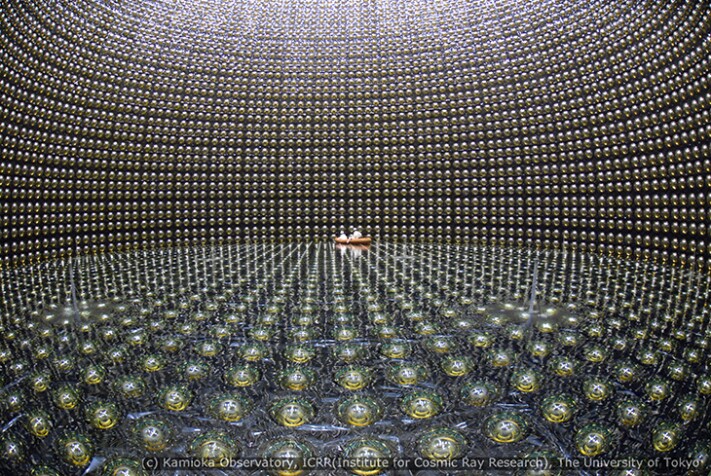
Super-Kamiokande detector
courtesy of Kamioka Observatory, ICRR (Institute for Cosmic Ray Research), The University of Tokyo
(Inside Science) -- The 2015 Nobel Prize in Physics has been awarded to a Japanese physicist and a Canadian physicist for discovering that abundant subatomic particles known as neutrinos can undergo changes in their identity, a process that requires the particles, once thought to be massless, to possess mass.
The prize goes jointly to Takaaki Kajita of the University of Tokyo in Japan and Arthur B. McDonald of Queen’s University in Kingston, Canada “for the discovery of neutrino oscillations, which shows that neutrinos have mass.” The two recipients were leaders of two major neutrino observatories: Kajita was part of the Super-Kamiokande collaboration in Japan, and McDonald led a group at the Sudbury Neutrino Observatory in Canada.
More details are available at http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/
Editor’s Note: Inside Science will provide detailed coverage of the 2015 Nobel Prize in a longer article to be issued later today.


